Case Study: Last-Mile Autonomous Delivery Robots
The Final Frontier For Today’s Booming E-Commerce  Comes In Last-Mile Autonomous Delivery Robots.
Comes In Last-Mile Autonomous Delivery Robots.
You are probably familiar with autonomous mobile robots (AMRs). They generally work in a manufacturing facility, or inventory warehouse, or other place where various, often mundane tasks need to be performed repeatedly. Thanks to machine vision, machine learning, and a few other technologies, AMRs have a big place in our present and future.
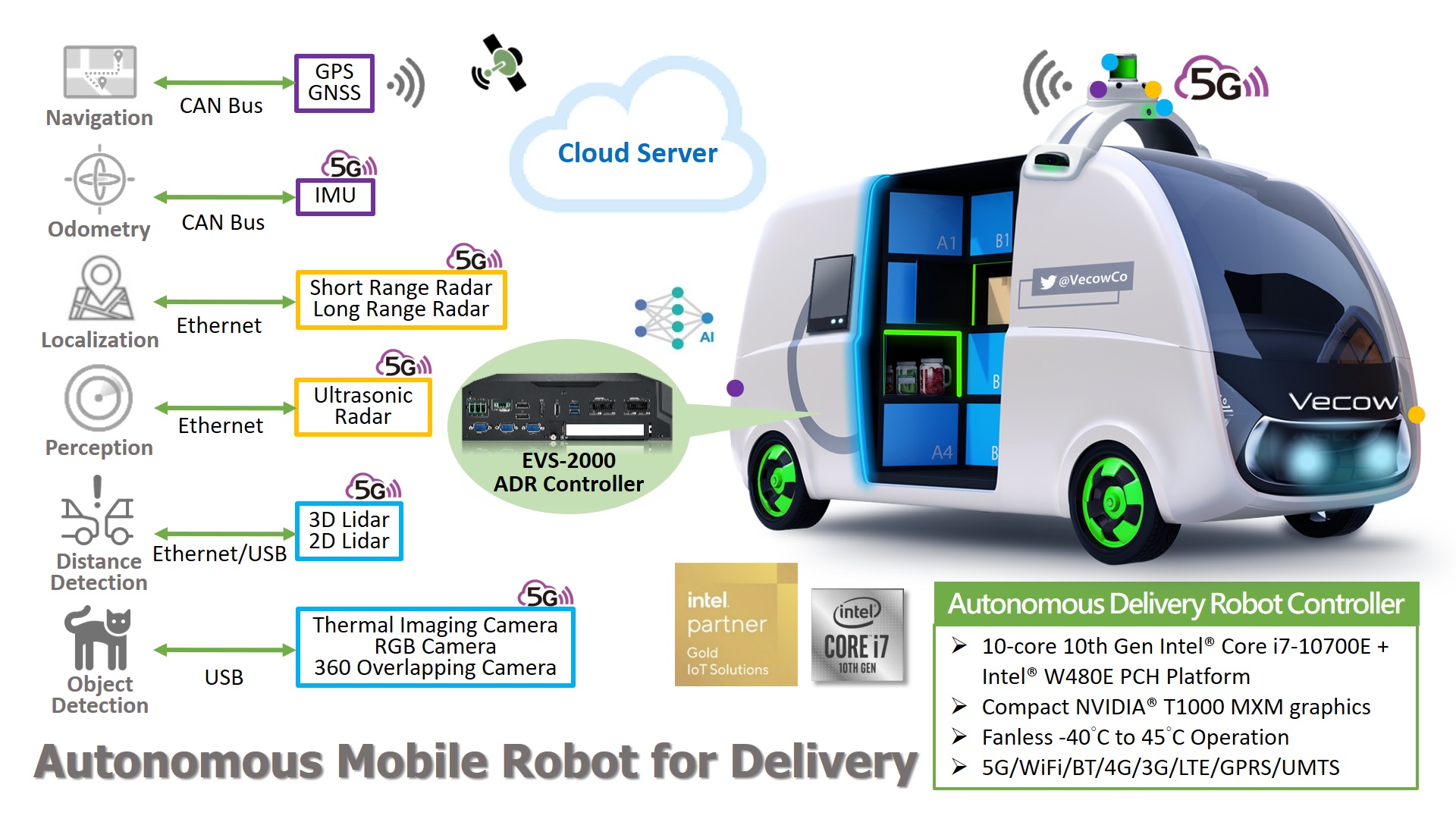
Last-mile autonomous delivery robots employ similar technologies; in some cases, they use identical technologies. This would include advanced sensors and cameras, GPS technology, two-way communications, artificial intelligence (AI), and machine learning algorithms to navigate roads, sidewalks, and other obstacles in rural, suburban, and urban environments. They must be designed to operate safely around pedestrians and other vehicles, with sensors and cameras to detect and avoid obstacles in their path.
In general, last-mile autonomous delivery robots are small, self-driving vehicles that deliver packages and goods directly to customers’ homes or to designated delivery points. The “goods” being delivered can range from your typical courier deliveries to food, medical supplies, and everything in between. The most obvious use case comes from today’s retail giants that offer same- and next-day delivery service. Those deliveries can come from a distribution center or can be dispersed from a larger vehicle. These robots can operate autonomously, or they can be controlled remotely by a human operator. In most cases, they are powered by a battery.
From the retailer’s perspective, that last mile often represents the most expensive and time-consuming segment of the delivery process, as it involves transporting goods from a centralized location to individual customers, often carrying a single product. And that delivery may be destined for a rural location, potentially taking a delivery person out of action for a long period of time.
 Last-mile autonomous delivery robots use a host of technologies to perform their duties. That includes machine vision, AI, and GPS.
Last-mile autonomous delivery robots use a host of technologies to perform their duties. That includes machine vision, AI, and GPS.
Growth Will Continue
The potential market for last-mile autonomous delivery robots is hard to determine because there are so many places where they could be used. Needless to say, the potential market is huge. Think about how many items get delivered, from short-range within a building, factory, school, hospital, etc., to longer ranges. And the recent pandemic put e-commerce and online shopping into the spotlight, with purchases growing significantly. In addition, there’s a desire to accelerate contactless delivery to reduce the risk of disease transmission.
According to one report (from McKinsey & Company), the global market for autonomous last-mile delivery is expected to reach $75 billion by 2025. And as technology improves, last-mile delivery robots will continue to improve and grow in use.
Technical Challenges Abound
From the supplier’s perspective, there are a host of challenges that need to be addressed and solved. They include:
・the need for a small and fanless platform that can potentially contain a graphics card
・object recognition to avoid obstacles, people, and vehicles, amongst other things
・the ability to operate in harsh environments, including dust, moisture, shock and vibration, and extreme temperatures
・upgradability, in terms of both hardware and software. The latter should be handled over the air (OTA) to nearly any location
Vecow Has the Answer
Vecow has come up with an embedded solution to tackle these challenges, starting with the company’s EVS-2000 platform. The EVS-2000 is a rugged, fanless embedded computer that’s designed for industrial applications that require lots of compute power and high reliability in any type of environment. It features an aluminum enclosure that can withstand shocks, vibrations, and extreme temperatures (ranging from -25°C to +55°C), even with fanless operation.
 The Vecow EVS-2000 is a rugged, fanless embedded computer that has the specs needed for last-mile autonomous delivery robot applications.
The Vecow EVS-2000 is a rugged, fanless embedded computer that has the specs needed for last-mile autonomous delivery robot applications.
The EVS-2000 is designed around an Intel Core i7-10700E microprocessor and can support up to 32 Gbytes of DDR4 DRAM. In addition, the platform contains a compact NVIDIA T1000 MXM graphics card that supports up to 896 CUDA processing cores to enable the visualization field and the plot, calculate the best possible routes, avoids obstacles, and plot maps, all key characteristics of last-mile autonomous delivery robots. In addition, last-mile autonomous robots are generally space constrained. Hence, the physical measurements of the EVS-2000 come into play—just 280 by 215 by 79 mm.
In addition, it boasts an Intel UHD Graphics P630 GPU that supports 4K display resolutions, making it suitable for most last-mile autonomous delivery robot applications. Its expansion options include a Mini PCIe slot and an M.2 slot for WWAN, WLAN, or CAN bus, allowing system designers to increase functionality or storage as needed and as it becomes available.
Hence, the EVS-2000 is more than equipped to handle the latest AI and machine vision applications. It offers various connectivity options, including Gigabit Ethernet, USB 3.0, serial ports, and HDMI/VGA display interfaces. The DC input voltage level ranges from 9 to 50 V with 80V surge protection.
Your Partner for Last-Mile Autonomous Delivery Robots
Vecow should be your partner for last-mile autonomous delivery robots for various reasons. First, the company’s products, such as the low-power EVS-2000, can operate reliably in almost any environment encountered, ensuring that they can operate consistently and without failure.
Second, Vecow's products aimed at this space are highly customizable, allowing OEMs to tailor their systems to meet their specific needs and environments, with faster (or more) CPUs, additional cameras, more storage, multiple I/O and graphics options, and so on.
The company has been working with customers on the latest demands in this space, many of which can be fulfilled by the EVS-2000 platforms. Vecow’s modularized computer boards and I/O allow for faster design turn-around times so its customers can quickly develop and improve their own products. Lastly, Vecow operates with a dedicated and experienced project team that provides trusted support in all technical phases, even after the robot has been deployed. Contact your local Vecow sales representative for more information.